1. Overview
1.概述
In this tutorial, we will see how to loop diagonally through a two-dimensional array. The solution that we provide can be used for a square two-dimensional array of any size.
在本教程中,我们将看到如何在一个二维数组中进行斜向循环。我们提供的解决方案可以用于任何大小的方形二维数组。
2. Two-Dimensional Array
2.二维阵列
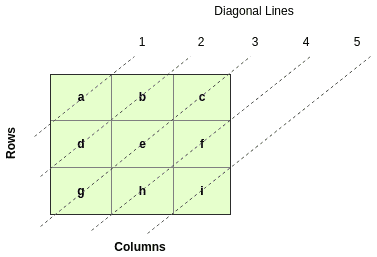
The key in working with elements of an array is knowing how to get a specific element from that array. For a two-dimensional array, we use row and column indices to get elements of an array. For this problem, we’ll use the following diagram to show how to get these elements.
处理数组元素的关键是知道如何从该数组中获得一个特定的元素。对于一个二维数组,我们使用行和列的索引来获取数组的元素。对于这个问题,我们将使用下面的图表来说明如何获得这些元素。
Next, we need to understand how many diagonal lines we have in our array, as seen in the diagram. We do this by first getting the length of one dimension of the array and then using that to get the number of diagonal lines (diagonalLines).
接下来,我们需要了解我们的数组中有多少条对角线,正如图中所示。我们首先得到数组中一个维度的长度,然后用它来得到对角线的数量(diagonalLines).。
We then use the number of diagonal lines to get the mid-point which will help in the search for row and column indices.
然后我们用对角线的数量来获得中点,这将有助于搜索行和列的索引。
In this example, the mid-point is three:
在这个例子中,中间点是3。
int length = twoDArray.length
int diagonalLines = (length + length) - 1
int midPoint = (diagonalLines / 2) + 13. Getting Row and Column Indices
3.获取行和列索引
To loop through the whole array, we start looping from 1 until the loop variable is less than or equal to the diagonalLines variable.
为了循环浏览整个数组,我们从1开始循环,直到循环变量小于或等于diagonalLines变量。
for (int i = 1; i <= diagonalLines; i++) {
// some operations
}Let’s also introduce the idea of the number of items in a diagonal line, calling it itemsInDiagonal. For example, line 3 in the diagram above has 3 items (g, e, c) and line 4 has 2 (h, f). This variable is incremented by 1 in the loop when loop variable i is less or equal to midPoint. It is then decremented by 1 otherwise.
我们也来介绍一下对角线上的项目数的概念,称之为itemsInDiagonal。例如,上图中第3行有3项(g,e,c),第4行有2项(h,f)。当循环变量i小于或等于midPoint时,这个变量在循环中被增加1。否则就减去1。
After incrementing or decrementing itemsInDiagonal, we then have a new loop with loop variable j. Variable j is incremented from 0 until it is less than itemsInDiagonal.
在递增或递减itemsInDiagonal之后,我们有一个新的循环,循环变量j。变量j从0开始递增,直到它小于itemsInDiagonal.。
We then use loop variables i and j to get the row and column indices. The logic of this calculation depends on whether loop variable i is greater than midPoint or not. When i is greater than midPoint, we also use the length variable to determine the row and column indices:
然后我们使用循环变量i 和j 来获得行和列的索引。这个计算的逻辑取决于循环变量i是否大于midPoint。当i 大于midPoint时,我们也使用length变量来确定行和列的索引。
int rowIndex;
int columnIndex;
if (i <= midPoint) {
itemsInDiagonal++;
for (int j = 0; j < itemsInDiagonal; j++) {
rowIndex = (i - j) - 1;
columnIndex = j;
items.append(twoDArray[rowIndex][columnIndex]);
}
} else {
itemsInDiagonal--;
for (int j = 0; j < itemsInDiagonal; j++) {
rowIndex = (length - 1) - j;
columnIndex = (i - length) + j;
items.append(twoDArray[rowIndex][columnIndex]);
}
}4. Conclusion
4.总结
In this tutorial, we have shown how to loop diagonally through a square two-dimensional array using a method that helps in getting row and column indices.
在本教程中,我们展示了如何使用一种有助于获得行和列索引的方法,在一个正方形二维数组中进行对角线循环。
As always, the full source code of the example is available over on GitHub.
一如既往,该示例的完整源代码可在GitHub上获取。