1. Overview
1.概述
In this tutorial, we’ll learn about the Model View Controller and Model View Presenter patterns. We’ll also discuss the differences between them.
在本教程中,我们将学习模型视图控制器和模型视图呈现器模式。我们还将讨论它们之间的区别。
2. Design Pattern and Architectural Pattern
2.设计模式和架构模式
2.1. Architectural Pattern
2.1.架构模式
Architectural patterns are general, reusable solutions to commonly occurring problems in software architecture. These have an extensive impact on the codebase.
架构模式是对软件架构中经常出现的问题的一般性、可重复使用的解决方案。这些对代码库有广泛的影响。
For example, these impact the software either horizontally or vertically. By horizontally, we mean how to structure the code inside a layer. Conversely, vertically means how a request is processed from outer layers to inner layers and back.
例如,这些对软件的影响要么是横向的,要么是纵向的。横向上,我们指的是如何构造一个层内的代码。相反,纵向是指如何将一个请求从外层处理到内层再返回。
Some of the more common architectural patterns are MVC, MVP, and MVVM.
一些比较常见的架构模式是MVC、MVP和MVVM。
2.2. Design Pattern
2.2.设计模式</b
Design patterns are usually associated with code-level commonalities. They provide various schemes for refining and building smaller subsystems.
设计模式通常与代码级的共性相关。它们为完善和构建更小的子系统提供了各种方案。
Additionally, design patterns are medium-scale tactics that flesh out some of the structure and behavior of entities and their relationships. Some commonly used design patterns are the singleton, factory, and builder patterns.
此外,设计模式是中等规模的战术,它充实了实体及其关系的一些结构和行为。一些常用的设计模式是singleton、factory,以及builder模式。
Design Patterns differ from Architectural Patterns in their scope. They’re more localized and have less impact on the codebase. Instead, they impact only a specific section of the codebase. In the next section, we’ll talk about why we use these patterns.
设计模式与架构模式的区别在于其范围。它们更加本地化,对代码库的影响更小。相反,它们只影响代码库的特定部分。在下一节中,我们将讨论为什么我们要使用这些模式。
3. Why MVC and MVP Patterns
3.为什么是MVC和MVP模式?
The main idea behind the use of these patterns is the separation of concerns between the business and UI layers. These patterns provide us with features like ease of testing. They also hide data access.
使用这些模式背后的主要想法是分离关注点 在业务层和UI层之间。这些模式为我们提供了诸如易于测试的功能。它们也隐藏了数据访问。
We can say they’re more adaptable to change by isolating the major components. However, the biggest drawbacks are adding complexity and the learning curve.
我们可以说,它们通过隔离主要部件,对变化的适应性更强。然而,最大的缺点是增加了复杂性和学习曲线。
4. MVC Pattern
4.MVC模式
In the MVC pattern, features are divided into three components based on three separate concerns. Firstly, the view is responsible for rendering UI elements. Secondly, the controller responds to UI actions. And the model handles business behaviors and state management.
在MVC模式中,基于三个独立的关注点,功能被分为三个部分。首先,视图负责渲染UI元素。其次,控制器响应UI动作。而模型处理业务行为和状态管理。
In most implementations, all three components can directly interact with each other. However, in some implementations, the controller is responsible for determining which view to display.
在大多数的实现中,这三个组件都可以直接相互作用。然而,在一些实现中,控制器负责决定显示哪个视图。
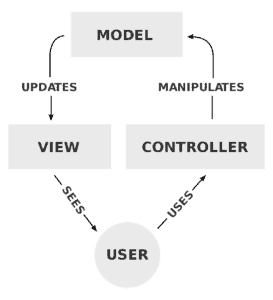
The diagram below shows the MVC flow of control:
下图显示了MVC的控制流。
The model represents the whole business logic layer. The view represents the data fetched from the model. In addition, it handles presentation logic. Lastly, the controller handles control flow logic and updates the model.
模型代表整个业务逻辑层。视图表示从模型中获取的数据。此外,它还处理表现逻辑。最后,控制器处理控制流逻辑并更新模型。
MVC doesn’t specify how the view and the model should be structured internally. Usually, the view layer is implemented in a single class.
MVC 没有规定视图和模型在内部应该如何结构化。通常情况下,视图层是在一个单一的类中实现的。
However, in that case, a couple of problems can arise:
然而,在这种情况下,会出现几个问题。
- The view and the model are tightly coupled. As a result, feature requirements of the view can easily drip down to the model and pollute the business logic layer
- The view is monolithic and usually couples tightly with the UI framework. Thus, unit testing the view becomes difficult
5. MVP Pattern
5.MVP模式
The MVP pattern is a UI presentation pattern based on the concepts of the MVC pattern. However, it doesn’t specify how to structure the whole system. It only dictates how to structure the view.
MVP模式是一种基于MVC模式概念的UI表现模式。然而,它并没有规定如何构造整个系统。它只规定了如何构造视图。
This pattern separates responsibilities across four components in general. Firstly the view is responsible for rendering UI elements. Secondly, the view interface is used to loosely couple the presenter from its view.
这种模式一般将责任分离到四个部分。首先视图负责渲染UI元素。其次,视图接口被用来将演示者与它的视图松散地联系起来。
Finally, the presenter interacts with the view and model, and the model is responsible for business behaviors and state management.
最后,演示者与视图和模型进行交互,而模型负责业务行为和状态管理。
In some implementations, the presenter interacts with a service (controller) layer to retrieve/persist the model. The view interface and service layer are commonly used to make writing unit tests for the presenter and the model easier.
在一些实现中,展示者与服务(控制器)层交互,以检索/保存模型。视图接口和服务层通常被用来使编写演示者和模型的单元测试更容易。
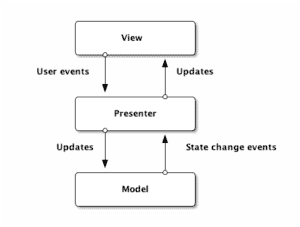
The diagram below shows the MVP flow of control:
下图显示了MVP的控制流。
The model is the same as in MVC and contains the business logic. The view is a passive interface that displays data. It sends user actions to the presenter.
模型与MVC中相同,包含业务逻辑。视图是一个被动的界面,显示数据。它将用户的操作发送到演示器。
The presenter sits between the model and view. It triggers business logic and enables the view to update. It receives data from the model and shows the same in the view. This makes testing the presenter much easier.
演示器位于模型和视图之间。它触发业务逻辑并使视图得以更新。它从模型中接收数据并在视图中显示相同的数据。这使得测试presenter更加容易。
Still, there are some problems with MVP:
不过,MVP还是有一些问题。
- The controller is often omitted. Because of the lack of a controller, control flow has also to be handled by the presenter. This makes the presenter responsible for two concerns: updating the model and presenting the model
- We can’t utilize data binding. If binding is possible with the UI framework, we should utilize it to simplify the presenter
6. MVC and MVP Implementation
6.MVC和MVP的实施</b
We’ll understand the patterns with a simple example. We’ve got a product that we need to show and update. These actions are handled differently in MVC and MVP.
我们将通过一个简单的例子来理解这些模式。我们有一个产品,我们需要展示和更新。这些动作在MVC和MVP中的处理方式是不同的。
6.1. The View Class
6.1.视图类
We have a simple view class that outputs the product details. The view class for both MVP and MVC are similar:
我们有一个简单的视图类来输出产品的详细信息。MVP和MVC的视图类都是类似的。
public class ProductView {
public void printProductDetails(String name, String description, Double price) {
log.info("Product details:");
log.info("product Name: " + name);
log.info("product Description: " + description);
log.info("product price: " + price);
}
}
6.2. MVP Model and Presenter Classes
6.2.MVP模型和演示者类
Let’s now define a Product class for MVP that is responsible for the business logic only:
现在让我们为MVP定义一个Product类,只负责业务逻辑。
public class Product {
private String name;
private String description;
private Double price;
//getters & setters
}The presenter class in MVP fetches the data from the model and passes it to the view:
MVP中的presenter类从模型中获取数据并将其传递给视图。
public class ProductPresenter {
private final Product product;
private final ProductView view;
//getters,setters & constructor
public void showProduct() {
productView.printProductDetails(product.getName(), product.getDescription(), product.getPrice());
}
}6.3. MVC Model Class
6.3.MVC模型类
For MVC, the difference is that the view will get the data from the model class instead of the presenter class in MVP.
对于MVC,区别在于视图将从模型类而不是MVP中的presenter类获得数据。
We can define a model class for MVC:
我们可以为MVC定义一个模型类。
public class Product {
private String name;
private String description;
private Double price;
private ProductView view;
//getters,setters
public void showProduct() {
view.printProductDetails(name, description, price);
}
}
Notice the showProduct() method. This method handles the data passing from model to view. In MVP, this is done in the presenter class, and in MVC, it’s done in the model class.
注意到showProduct()方法。这个方法处理从模型到视图的数据传递。在MVP中,这是在presenter类中完成的,而在MVC中,它是在模型类中完成的。
7. Comparison Between MVC and MVP
7.MVC与MVP的比较</b
There aren’t a whole lot of differences between MVC and MVP. Both patterns focus on separating responsibility across multiple components, hence, promoting loose coupling of the UI (View) from the business layer (Model).
MVC和MVP之间并没有太多的区别。两种模式都注重在多个组件之间分离责任,因此,促进了用户界面(视图)与业务层(模型)的松散耦合。
The major differences are how the patterns are implemented and in some advanced scenarios. Let’s look at some of the key differences:
主要的区别在于如何实现这些模式以及在一些高级场景中。让我们看看一些关键的差异。
- Coupling: The view and the model are tightly coupled in MVC but loosely coupled in MVP
- Communication: In MVP, communication between the View-Presenter and Presenter-Model happens via an interface. However, the controller and view layer falls in the same activity/fragment in MVC
- User Input: In MVC, user inputs are handled by the Controller that instructs the model for further operations. But in MVP, user inputs are handled by the view that instructs the presenter to call appropriate functions
- Type of Relation: A many-to-one relationship exists between the controller and view. One Controller can select different views based upon required operations in MVC. On the other hand, the presenter and view have a one-to-one relationship in MVP, where one presenter class manages one view at a time
- Main Component: In MVC, the controller is in charge. It creates the appropriate view and interacts with the model according to the user’s request. On the contrary, in MVP, the view is in charge. The view call methods on the presenter, which further directs the model
- Unit Testing: Due to tight coupling, MVC has limited support for unit testing. On the other hand, unit Testing is well supported in MVP
8. Why MVP Has an Edge Over MVC
8.为什么MVP比MVC有优势</b
MVP has the slight upper hand over MVC in that it can break down our application into modules. Thus, we can avoid having to create views constantly. In other words, MVP can help to make our views reusable.
MVP比MVC略胜一筹,因为它可以将我们的应用程序分解成模块。因此,我们可以避免不断地创建视图。换句话说,MVP可以帮助我们实现视图的重复使用。
9. Conclusion
9.结论
In this tutorial, we’ve seen the MVC and MVP architectural patterns and a comparison between them.
在本教程中,我们已经看到了MVC和MVP架构模式以及它们之间的比较。
The example code is available over on GitHub.
示例代码可在GitHub上获得over。