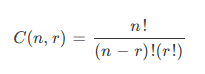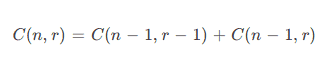1. Introduction
1.绪论
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss the solution to the k-combinations problem in Java.
在本教程中,我们将讨论Java中k-combinations问题的解决方案。
First, we’ll discuss and implement both recursive and iterative algorithms to generate all combinations of a given size. Then we’ll review solutions using common Java libraries.
首先,我们将讨论并实现递归和迭代算法,以生成特定大小的所有组合。然后,我们将审查使用普通Java库的解决方案。
2. Combinations Overview
2.组合概述
Simply put, a combination is a subset of elements from a given set.
简单地说,组合是一个给定集合中的元素子集。
Unlike permutations, the order in which we choose the individual elements doesn’t matter. Instead, we only care whether a particular element is in the selection.
与排列组合不同,我们选择各个元素的顺序并不重要。相反,我们只关心一个特定的元素是否在选择中。
For example, in a card game, we have to deal 5 cards out of the pack consisting of 52 cards. We have no interest in the order in which the 5 cards were selected. Rather, we only care which cards are present in the hand.
例如,在一个纸牌游戏中,我们必须从由52张牌组成的包中发5张牌。我们对这5张牌的选择顺序没有兴趣。相反,我们只关心手上有哪些牌。
Some problems require us to evaluate all possible combinations. In order to do this, we enumerate the various combinations.
有些问题要求我们评估所有可能的组合。为了做到这一点,我们列举了各种组合。
The number of distinct ways to choose “r” elements from the set of “n” elements can be expressed mathematically with the following formula:
从 “n “个元素的集合中选择 “r “个元素的不同方式的数量可以用以下公式来表示:。
Therefore, the number of ways to choose elements can grow exponentially in the worst case. Hence, for large populations, it may not be possible to enumerate the different selections.
因此,在最坏的情况下,选择元素的方法的数量会呈指数级增长。因此,对于大群体来说,可能无法列举出不同的选择方式。
In such cases, we may randomly select a few representative selections. The process is called sampling.
在这种情况下,我们可以随机地选择一些有代表性的选题。这个过程被称为抽样。
Next, we’ll review the various algorithms to list combinations.
接下来,我们将回顾一下列表组合的各种算法。
3. Recursive Algorithms to Generate Combinations
3.产生组合的递归算法
Recursive algorithms usually work by partitioning a problem into similar smaller problems. This process continues until we reach the terminating condition, which is also the base case. Then we solve the base case directly.
递归算法通常通过将一个问题分割成类似的小问题来工作。这个过程一直持续到我们达到终止条件,这也是基本情况。然后我们直接解决基本情况。
We’ll discuss two ways to subdivide the task of choosing elements from a set. The first approach divides the problem in terms of the elements in the set. The second approach divides the problem by tracking the selected elements only.
我们将讨论将从一个集合中选择元素的任务进行细分的两种方法。第一种方法是以集合中的元素来划分问题。第二种方法仅通过跟踪所选元素来划分问题。
3.1. Partitioning by Elements in the Entire Set
3.1.按整个集合中的元素进行划分
Let’s divide the task of selecting “r” elements from “n” items by inspecting the items one by one. For each item in the set, we can either include it in the selection or exclude it.
让我们把从”n”项中选择”r”元素的任务划分开来,逐一检查这些项目。对于集合中的每个项目,我们可以将其纳入选择范围,也可以将其排除在外。
If we include the first item, then we need to choose “r – 1″ elements from the remaining “n – 1″ items. On the other hand, if we discard the first item, then we need to select “r” elements out of the remaining “n – 1″ items.
如果我们包括第一项,那么我们需要从剩余的”n – 1″项中选择 “r – 1″元素。另一方面,如果我们放弃第一个项目,那么我们需要从剩余的”n – 1″项目中选择”r”元素。
This can be mathematically expressed as:
这可以在数学上表示为:。
Now, let’s look into the recursive implementation of this approach:
现在,让我们来看看这种方法的递归实现。
private void helper(List<int[]> combinations, int data[], int start, int end, int index) {
if (index == data.length) {
int[] combination = data.clone();
combinations.add(combination);
} else if (start <= end) {
data[index] = start;
helper(combinations, data, start + 1, end, index + 1);
helper(combinations, data, start + 1, end, index);
}
}The helper method makes two recursive calls to itself. The first call includes the current element. The second call discards the current element.
helper方法对自己进行了两次递归调用。第一次调用包括当前元素。第二次调用丢弃当前元素。
Next, let’s write the combination generator using this helper method:
接下来,让我们使用这个helper方法编写组合生成器。
public List<int[]> generate(int n, int r) {
List<int[]> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
helper(combinations, new int[r], 0, n-1, 0);
return combinations;
}In the above code, the generate method sets up the first call to the helper method and passes the appropriate parameters.
在上面的代码中,generate方法设置了对helper方法的第一次调用,并传递适当的参数。
Next, let’s call this method to generate combinations:
接下来,让我们调用这个方法来生成组合。
List<int[]> combinations = generate(N, R);
for (int[] combination : combinations) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(combination));
}
System.out.printf("generated %d combinations of %d items from %d ", combinations.size(), R, N);On executing the program, we get the following output:
在执行该程序时,我们得到以下输出。
[0, 1]
[0, 2]
[0, 3]
[0, 4]
[1, 2]
[1, 3]
[1, 4]
[2, 3]
[2, 4]
[3, 4]
generated 10 combinations of 2 items from 5Finally, let’s write the test case:
最后,我们来写一下测试用例。
@Test
public void givenSetAndSelectionSize_whenCalculatedUsingSetRecursiveAlgorithm_thenExpectedCount() {
SetRecursiveCombinationGenerator generator = new SetRecursiveCombinationGenerator();
List<int[]> selection = generator.generate(N, R);
assertEquals(nCr, selection.size());
}It is easy to observe that the stack size required is the number of elements in the set. When the number of elements in the set is large, say, greater than the maximum call stack depth, we’ll overflow the stack and get a StackOverflowError.
很容易观察到,所需的堆栈大小是集合中元素的数量。当集合中的元素数量很大时,比如说,大于最大的调用堆栈深度,我们将溢出堆栈,得到一个StackOverflowError。。
Therefore, this approach doesn’t work if the input set is large.
因此,如果输入集很大,这种方法就不起作用。
3.2. Partitioning by Elements in the Combination
3.2.按组合中的元素进行划分
Instead of tracking the elements in the input set, we’ll divide the task by tracking the items in the selection.
与其跟踪输入集中的元素,我们将通过跟踪选择中的项目来分担任务。
First, let’s order the items in the input set using indices “1” to “n”. Now, we can choose the first item from the first “n-r+1″ items.
首先,让我们用指数 “1 “到”n”对输入集合中的项目进行排序。现在,我们可以从第一个”n-r+1″项中选择第一个项目。
Let’s assume that we chose the kth item. Then, we need to choose “r – 1″ items from the remaining “n – k” items indexed “k + 1″ to “n”.
让我们假设我们选择了第k个项目。然后,我们需要从剩余的”n – k”/em>项中选择”r – 1″项,索引为”k + 1″至”n”/em>。
We express this process mathematically as:
我们将这一过程用数学方法表示为:。
Next, let’s write the recursive method to implement this approach:
接下来,让我们编写递归方法来实现这种方法:。
private void helper(List<int[]> combinations, int data[], int start, int end, int index) {
if (index == data.length) {
int[] combination = data.clone();
combinations.add(combination);
} else {
int max = Math.min(end, end + 1 - data.length + index);
for (int i = start; i <= max; i++) {
data[index] = i;
helper(combinations, data, i + 1, end, index + 1);
}
}
}In the above code, the for loop chooses the next item, Then, it calls the helper() method recursively to choose the remaining items. We stop when the required number of items have been selected.
在上面的代码中,for 循环选择了下一个项目,然后,它递归地调用helper()方法来选择剩余的项目。我们在选择了所需数量的项目后停止。
Next, let’s use the helper method to generate selections:
接下来,让我们使用helper方法来生成选择。
public List<int[]> generate(int n, int r) {
List<int[]> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
helper(combinations, new int[r], 0, n - 1, 0);
return combinations;
}Finally, let’s write a test case:
最后,我们来写一个测试用例。
@Test
public void givenSetAndSelectionSize_whenCalculatedUsingSelectionRecursiveAlgorithm_thenExpectedCount() {
SelectionRecursiveCombinationGenerator generator = new SelectionRecursiveCombinationGenerator();
List<int[]> selection = generator.generate(N, R);
assertEquals(nCr, selection.size());
}The call stack size used by this approach is the same as the number of elements in the selection. Therefore, this approach can work for large inputs so long as the number of elements to be selected is less than the maximum call stack depth.
这种方法所使用的调用堆栈大小与选择中的元素数量相同。因此,只要要选择的元素数量少于最大的调用堆栈深度,这种方法就能适用于大的输入。
If the number of elements to be chosen is also large, this method won’t work.
如果要选择的元素数量也很大,这个方法就不灵了。
4. Iterative Algorithm
4.迭代算法
In the iterative approach, we start with an initial combination. Then, we keep generating the next combination from the current one until we have generated all combinations.
在迭代方法中,我们从一个初始组合开始。然后,我们不断从当前的组合中生成下一个组合,直到我们生成了所有的组合。
Let’s generate the combinations in lexicographic order. We start with the lowest lexicographic combination.
让我们按词法顺序生成组合。我们从最低的词法组合开始。
In order to get the next combination from the current one, we find the rightmost location in the current combination that can be incremented. Then, we increment the location and generate the lowest possible lexicographic combination to the right of that location.
为了从当前的组合中得到下一个组合,我们找到当前组合中可以递增的最右边的位置。然后,我们递增该位置,并生成该位置右边的最低可能的词法组合。
Let’s write the code which follows this approach:
让我们写一下遵循这种方法的代码。
public List<int[]> generate(int n, int r) {
List<int[]> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
int[] combination = new int[r];
// initialize with lowest lexicographic combination
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
combination[i] = i;
}
while (combination[r - 1] < n) {
combinations.add(combination.clone());
// generate next combination in lexicographic order
int t = r - 1;
while (t != 0 && combination[t] == n - r + t) {
t--;
}
combination[t]++;
for (int i = t + 1; i < r; i++) {
combination[i] = combination[i - 1] + 1;
}
}
return combinations;
}Next, let’s write the test case:
接下来,我们来写测试案例。
@Test
public void givenSetAndSelectionSize_whenCalculatedUsingIterativeAlgorithm_thenExpectedCount() {
IterativeCombinationGenerator generator = new IterativeCombinationGenerator();
List<int[]> selection = generator.generate(N, R);
assertEquals(nCr, selection.size());
}Now, let us use some Java libraries to solve the problem.
现在,让我们使用一些Java库来解决这个问题。
5. Java Libraries Implementing Combinations
5.实现组合的Java库
As far as possible, we should reuse existing library implementations instead of rolling out our own. In this section, we’ll explore the following Java libraries that implement combinations:
尽可能地,我们应该重复使用现有的库实现,而不是推出我们自己的库。在本节中,我们将探讨以下实现组合的Java库。
- Apache Commons
- Guava
- CombinatoricsLib
5.1. Apache Commons
5.1.Apache Commons
The CombinatoricsUtils class from Apache Commons provides many combination utility functions. In particular, the combinationsIterator method returns an iterator that will generate combinations in lexicographic order.
来自Apache Commons的CombinatoricsUtils类提供了许多组合实用函数。特别是,combinationsIterator方法返回一个迭代器,该迭代器将按词典顺序生成组合。
First, let’s add the Maven dependency commons-math3 to the project:
首先,让我们把Maven依赖commons-math3加入项目。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-math3</artifactId>
<version>3.6.1</version>
</dependency>Next, let’s use the combinationsIterator method to print the combinations:
接下来,让我们使用combinationsIterator方法来打印组合。
public static void generate(int n, int r) {
Iterator<int[]> iterator = CombinatoricsUtils.combinationsIterator(n, r);
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
final int[] combination = iterator.next();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(combination));
}
}5.2. Google Guava
5.2. Google Guava
The Sets class from Guava library provides utility methods for set-related operations. The combinations method returns all subsets of a given size.
Guava库中的Sets类为集合相关的操作提供了实用方法。组合方法返回给定大小的所有子集。
First, let’s add the maven dependency for the Guava library to the project:
首先,让我们把Guava库的maven依赖性添加到项目中。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>31.0.1-jre</version>
</dependency>Next, let’s use the combinations method to generate combinations:
接下来,让我们使用combinations方法来生成组合。
Set<Set<Integer>> combinations = Sets.combinations(ImmutableSet.of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5), 3);Here, we are using the ImmutableSet.of method to create a set from the given numbers.
这里,我们使用ImmutableSet.of方法,从给定的数字中创建一个集合。
5.3. CombinatoricsLib
5.3.组合学库(CombinatoricsLib
CombinatoricsLib is a small and simple Java library for permutations, combinations, subsets, integer partitions, and cartesian product.
CombinatoricsLib是一个小而简单的Java库,用于处理排列、组合、子集、整数分割和笛卡尔积。。
To use it in the project, let’s add the combinatoricslib3 Maven dependency:
要在项目中使用它,让我们添加combinatoricslib3Maven依赖项。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.dpaukov</groupId>
<artifactId>combinatoricslib3</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>Next, let’s use the library to print the combinations:
接下来,让我们使用该库来打印组合:。
Generator.combination(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.simple(3)
.stream()
.forEach(System.out::println);This produces the following output on execution:
这在执行时产生以下输出。
[0, 1, 2]
[0, 1, 3]
[0, 1, 4]
[0, 1, 5]
[0, 2, 3]
[0, 2, 4]
[0, 2, 5]
[0, 3, 4]
[0, 3, 5]
[0, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 4]
[1, 2, 5]
[1, 3, 4]
[1, 3, 5]
[1, 4, 5]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 5]
[2, 4, 5]
[3, 4, 5]More examples are available at combinatoricslib3-example.
更多的例子可在combinatoricslib3-example。
6. Conclusion
6.结语
In this article, we implemented a few algorithms to generate combinations.
在这篇文章中,我们实现了一些算法来生成组合。
We also reviewed a few library implementations. Typically, we’d use these instead of rolling our own.
我们还审查了一些库的实现。通常情况下,我们会使用这些,而不是推出我们自己的。
As usual, the full source code can be found over on GitHub.
像往常一样,完整的源代码可以在GitHub上找到超过。